Excretory-system
EXCRETORY SYSTEM OF RANA (FROG) AND SCOLIODON(SHARK FISH)-SIMILARITIES AND DIFFERENCES
Kidneys are the major excretory organs in all vertebrates. Some other organs such as lungs, gills, liver, intestine and skin also remove certain waste materials besides their normal functions. These are also known as the accessory excretory organs. Both shark and frog are anamniotic animals.
The kidneys lie dorsal to the coelom and are composed of large number of renal or uriniferous tubules. A uriniferous tubule typically consists of three regions - a ciliated peritoneal funnel, a malpighian body and a ciliated convoluted tube. The malpighian body is a two layered cup, the 'Bowman's capsule' containing a mass of capillaries the 'glomerulus'. The convoluted tube opens into a Longitudinal duct which extends backwards and opens into the cloaca. The excretory organs remove the nitrogenous waste products formed during the metabolic activities from time to time. If these products are not removed from the body, they are changed to toxic substances.
frog-excretory-system
shark-fish-excretory-system
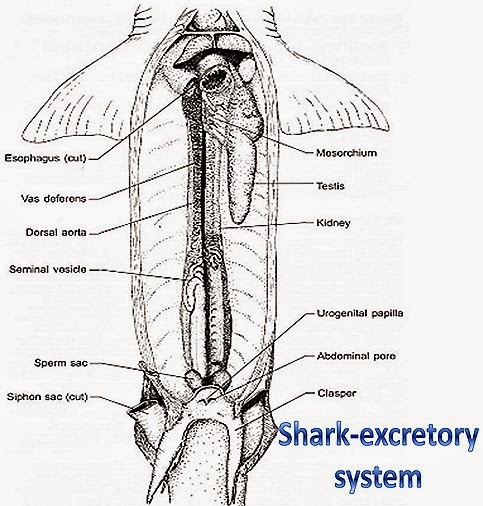
EXCRETORY SYSTEM OF FISH
EXCRETORY SYSTEM OF FROG
1. Paired kidneys are very long and ribbon like. 1. Paired kidneys are short and roughly oval in shape.
2. Each kidney is differentiated into a small non-renal part (genital part) and a long posterior renal part. The two parts exhibit morphological difference. 2. Each kidney possesses genital as well as renal region. But these are not morphologically differentiated.
3. The kidneys are uriniferous 'Opisthonephros' but functional Mesonephros. 3. The kidneys are mesonephros.
4. Some uriniferous tubules retain peritoneal funnel 4. The peritoneal funnels are absent.
5. The uriniferous tubules have a specialised urea - absorbing segment. 5. The urea-absorbing segment is absent.
6. Uriniferous tubules lead into special tubes - the urinary ducts (ureters). These are distinct from wolffian ducts. 6. Uriniferous tubules lead into the wolffian ducts.
7. Ureters run back ward over the ventral surface of the kidneys. 7. Wolffian ducts leave outer border of kidneys and run backward.
8. Ureters are independent ducts to carry urine from the kidneys to the Urinogenital sinus'. 8. The ureters serve for the passage of genital elements as well as urine. So they are known as urino-genital ducts.Urino genital sinus is absent.
9. The urinary bladder is absent. 9. A large bilobed urinary bladder is present. It opens into the cloaca opposite the openings of the ureters.
10.The urine is hypotonic to blood. 10. The urine is hypertonic to blood.
11.Scoliodon is an ureotelic animal.The endproduct of nitrogen metabolism is urea. A large Quantity of urea is retained in the body as an adaptation to marine life.Excess of urea is excreted chiefly through its gills.
11. Frog is also ureotelic animal. It excretes urine from the cloaca in the form of urea.
arterial system of frog and fish-comparison
There are no products listed under this category.
